TRANSFORMING
THE FUTURE
#1 INTERNATIONAL MOBILITY ACADEMY
Complete modular solution integrating all aspects of net-zero fleet transition
ACADEMY
EVUNI franchise is powered by a skills development engine at the core built on fully accredited qualifications structured within the SAQA qualifications framework aligned with the Bologna Process that 47 countries are participating in. The curriculum provides learners with the opportunity to grow from level 1 to 7 with a diversity of courses including the full spectrum of skills requirements within the net-zero mobility and energy sector. The EVUNI open platform (EOP) enables instant plugins for TVET colleges (technical and vocational education and training), accredited SDPs (skills development providers), universities, teachers, FAM providers (facilitation, assessment & moderation) , domain experts, accreditation institutions, workplace experience providers, technology & financial services. The EVUNI platform is built on the world’s most widely used learning platform with more than 213 million users worldwide. EVUNI courses may be accessed online in all 195 countries worldwide. Delivery includes 24×7 online courses in addition to interactive classes and mentorship by top industry specialists. The EOP instantly mobilizes a multi-billion dollar international infrastructure and intellectual property investment within the education, skills development and green mobility and energy sector.
Most advanced and complete curriculum within the industry
EVC specialises in the full suite of fleet technology
Curriculum is technology driven incorporating latest technology & methodologies
Frictionless elearning built on the world’s number 1 LMS platform
Current, relevant content consistently updated by industry experts
Courses include workplace experience at with accredited global & local partners
Work-ready skills that advances the industry
Outcome with the highest level of employment security and earnings.
Content and training delivery is dynamically structured for global deployment
Localization of accreditations for scaled international deployment
Fully accredited QCTO qualifications & and specialised new-skills
Reskill existing workforce, preventing inequities, preserving talent & jobs
Mobility automation & technology is creating risks & opportunities
The mobility sector workforce requires new skills to adapt
Accessible quality training fosters equity in transition
Areas within the mobility sector is at high risk of creating further inequities
Bus drivers in the US are most at risk & earning minimum wage
We reskill the workforce, preventing inequities, preserving talent & jobs
New skills enables driver retention & better wages
A diversity of new skills are required within the ecosystem
The United States have 15.3 million registered trucks & buses
There are approximately 9 million directly affected workers
This affects + US$ 500b/year in wage expenses & + US$ 14b/yr in training & skills
Less than 1% are currently powered through battery electric & fuel cell powertrains
The transition will impact & transform communities.
Transition demands skills to operate and maintain vehicles and infrastructure
Extensive safety training required to work with high voltage batteries & hydrogen systems.
New driving techniques, charging protocols, and maintenance considerations
Training diesel and gasoline technician talent on electric drive systems is key
An NREL case study (NASEM 2018) showed an impact of + 50% on energy consumption based on driving technique between 2 drivers on same route
Training requirements includes:
- Drivers/Operators
- Logistical support
- Automotive technicians
- Electricians
- Vehicle suppliers/dealers
- Command & control technicians
- Skills & training providers
- Safety & first responders
EV College is an international high tech mobility academy
The head office is located in Singapore driving the technology & delivery engine
Frictionless on-line course delivery built on the world’s best open LMS platform
Integrated practical workplace experience through global & local industry partners
EV College specialises in the full suite of fleet technology training
Our content is the most advanced and complete within the mobility industry
Curriculum is technology driven incorporating latest technology & methodologies
Current, relevant content consistently updated by industry experts
Our objective is to deliver work-ready skills that advances the industry
The outcome is the highest level of employment security and earnings.
Content and training delivery is dynamically structured for global deployment
Localization of accreditations for scaled international deployment
Fully accredited QCTO qualifications & and specialised new-skills
Reskill existing workforce, preventing inequities, preserving talent & jobs
The United States is a priority focus area during phase 1
The United States have 15.3 million registered trucks & buses
There are approximately 9 million directly affected workers
This affects + US$ 500b/year in wage expenses & + US$ 14b/yr in training & skills
Less than 1% are currently powered through battery electric & fuel cell powertrains
The transition will impact & transform communities.
Transition demands skills to operate and maintain vehicles and infrastructure
Extensive safety training required to work with high voltage batteries & hydrogen systems.
New driving techniques, charging protocols, and maintenance considerations
Training diesel and gasoline technician talent on electric drive systems is key
An NREL case study (NASEM 2018) showed an impact of + 50% on energy consumption based on driving technique between 2 drivers on same route
Training requirements includes:
- Drivers/Operators
- Logistical support
- Automotive technicians
- Electricians
- Vehicle suppliers/dealers
- Command & control technicians
- Skills & training providers
- Safety & first responders
The academy provides training & skills within the following modules:
Insights & consulting module
Insights audit report (IAR) – comprehensive fleet assessment including 7 reports on all aspects of fleet operations
Vehicle module that includes:
- Powertrain evaluation (IAR 1 battery electric versus fuel cell)
- Federal & state vehicle incentive assessment
- Vehicle assessment (IAR2) including current fleet type, age & options
- Repower engineering of ICB vehicles (battery electric or fuel cell conversion of internal combustion engines & bus reconditioning)
- Vehicle maintenance
- New vehicle sales (battery electric or fuel cell)
- Vehicle market – trade in on ICB vehicles for conversion & resale
- Vehicle training (drivers, technicians, controllers)
- Fleet management including telematics & fleet & asset management software
- Vehicle finance, lease & partnership solutions
Infrastructure module includes:
- Infrastructure evaluation (IAR 3 & IAR 4)
- Electric versus Hydrogen infrastructure evaluation
- Federal & state infrastructure incentive assessment
- Grid availability & pricing analysis
- Hydrogen supply assessment
- Route & charge station analysis
- Depot versus on-route charge station analysis
- Modular charge station supply, engineering & maintenance ( Electric & Hydrogen)
- Infrastructure command & control systems
- Training (charge station/H2 depot technicians, controllers )
- Infrastructure finance, lease & partnership solutions
Power module includes:
- Infrastructure evaluation (IAR 3 & IAR 4)
- Electric versus Hydrogen infrastructure evaluation
- Federal & state infrastructure incentive assessment
- Grid availability & pricing analysis
- Hydrogen supply assessment
- Route & charge station analysis
- Depot versus on-route charge station analysis
- Modular power station supply, engineering & maintenance ( Electric & Hydrogen with PV or biomass powered)
- Infrastructure command & control systems
- Training (electric/H2 technicians, controllers )
- Infrastructure finance, lease & partnership solutions
Fleet management module includes:
Open system architecture enabling seamless integration with legacy telematics & systems
- Fleet management systems evaluation (IAR 5)
- Data-driven efficiency & Mobility electrification methodologies
- IoT powered integrated fleet management
- Seamless integration to existing telematics systems
- Fleet performance optimization (reduced fuel & maintenance costs)
- Training (telematics, software & controllers )
- Fleet management finance, lease & partnership solutions
- Modular systems enabling comprehensive command & control on all aspects of fleet operations including
- Telematics
- Fleet, infrastructure & asset management
- Expense & cost control
- Employee scheduling, training & wages
- Customer booking, payment collection & experience
Training & qualification module
- Most advanced and complete education within the industry
- Fully accredited qualifications and specialised new-skills programs.
- Built on the world’s number 1 LMS platform (Learner Management Software)
- Headed up by industry experts
- Dynamic global content and training delivery with localization of accreditations
- Most current and relevant international technology and skills requirements.
- Training includes workplace experience through global & local partners
- Work-ready skills that advances the industry
- Highest level of employment security and earnings.
Bank & Business module
EVC provides dynamic project finance, business model & partnership options.
Partnership options include:
- OMT (Operate-Maintain-Transfer)
- BT (Build Transfer)
- BOT (Build Operate Transfer)
- LDO (Lease-Develop-Operate)
- BOLT (Build-Operate-Lease-Transfer)
- BOOT (Build Own Operate Transfer)
- BOO (Build Own Operate).
The EV University (“EVUNI”) is an international academy delivering next generation mobility skills development specializing in fleet electrification.
EVUNI provides the most advanced specialised skills development within the Net-zero mobility sector.
The EVUNI curriculum offers a full spectrum of qualifications that includes all aspects of modular fleet electrification systems including:
- fleet electrification insights & consulting
- fleet management technology
- battery electric repower engineering
- fuel cell repower engineering
- modular electric charging
- modular hydrogen dispensing
- modular solar electricity production
- modular biomass electricity & biochar production with carbon credits
- modular green hydrogen production
- finance & business modeling
- modular franchise business units
- marketplace (new, trade-in & refurbishment of EVs)
- powertrain, equipment & vehicle supply chain management
- new venture including sports & hobby repowering
- advanced EV driver training
- high voltage & hydrogen systems safety
- mobility teacher training
The EVUNI curriculum is engineered on an international NQF (national qualifications framework) system aligned with the Bologna Process that 47 countries are participating in. Furthermore the curriculum has a foundation constructed on fully accredited QCTO skills, courses and occupational qualifications.
The platform is taken to an outstanding level through specialisation within the net-zero mobility sector that includes the most current technology & trends.
Qualifications are integrated with workplace experience at accredited EVUNI partners internationally. EVUNI graduates are equipped to thrive in the new world with outstanding skills that enable employment/income security, higher earnings, job satisfaction and increased quality of life. Graduates are equipped to contribute towards a net-zero vision that will transform the planet into a cleaner, healthier & safer home for future generations.
TVET (technical and vocational education and training) refers to all forms and levels of education and training which provide knowledge and skills related to occupations in various sectors of economic and social life through formal, non-formal and informal learning methods in both school-based and work-based learning contexts. To achieve its aims and purposes, TVET focuses on the learning and mastery of specialized techniques and the scientific principles underlying those techniques, as well as general knowledge, skills and values.
Vocational education is education that prepares people for a skilled craft as an artisan, trade as a tradesperson, or work as a technician. Vocational education can also be seen as that type of education given to an individual to prepare that individual to be gainfully employed or self employed with requisite skill.
Most advanced and complete curriculum within the industry
EVC specialises in the full suite of fleet technology
Curriculum is technology driven incorporating latest technology & methodologies
Frictionless elearning built on the world’s number 1 LMS platform
Current, relevant content consistently updated by industry experts
Courses include workplace experience at with accredited global & local partners
Work-ready skills that advances the industry
Outcome with the highest level of employment security and earnings.
Content and training delivery is dynamically structured for global deployment
Localization of accreditations for scaled international deployment
Fully accredited QCTO qualifications & and specialised new-skills
Reskill existing workforce, preventing inequities, preserving talent & jobs
The United States have 15.3 million registered trucks & buses
There are approximately 9 million directly affected workers
This affects + US$ 500b/year in wage expenses & + US$ 14b/yr in training & skills
Less than 1% are currently powered through battery electric & fuel cell powertrains
The transition will impact & transform communities.
Transition demands skills to operate and maintain vehicles and infrastructure
Extensive safety training required to work with high voltage batteries & hydrogen systems.
New driving techniques, charging protocols, and maintenance considerations
Training diesel and gasoline technician talent on electric drive systems is key
An NREL case study (NASEM 2018) showed an impact of + 50% on energy consumption based on driving technique between 2 drivers on same route
Training requirements includes:
- Drivers/Operators
- Logistical support
- Automotive technicians
- Electricians
- Vehicle suppliers/dealers
- Command & control technicians
- Skills & training providers
- Safety & first responders
EV College is an international high tech mobility academy
The head office is located in Singapore driving the technology & delivery engine
Frictionless on-line course delivery built on the world’s best open LMS platform
Integrated practical workplace experience through global & local industry partners
EV College specialises in the full suite of fleet technology training
Our content is the most advanced and complete within the mobility industry
Curriculum is technology driven incorporating latest technology & methodologies
Current, relevant content consistently updated by industry experts
Our objective is to deliver work-ready skills that advances the industry
The outcome is the highest level of employment security and earnings.
Content and training delivery is dynamically structured for global deployment
Localization of accreditations for scaled international deployment
Fully accredited QCTO qualifications & and specialised new-skills
Reskill existing workforce, preventing inequities, preserving talent & jobs
The United States is a priority focus area during phase 1
The United States have 15.3 million registered trucks & buses
There are approximately 9 million directly affected workers
This affects + US$ 500b/year in wage expenses & + US$ 14b/yr in training & skills
Less than 1% are currently powered through battery electric & fuel cell powertrains
The transition will impact & transform communities.
Transition demands skills to operate and maintain vehicles and infrastructure
Extensive safety training required to work with high voltage batteries & hydrogen systems.
New driving techniques, charging protocols, and maintenance considerations
Training diesel and gasoline technician talent on electric drive systems is key
An NREL case study (NASEM 2018) showed an impact of + 50% on energy consumption based on driving technique between 2 drivers on same route
Training requirements includes:
- Drivers/Operators
- Logistical support
- Automotive technicians
- Electricians
- Vehicle suppliers/dealers
- Command & control technicians
- Skills & training providers
- Safety & first responders
The academy provides training & skills within the following modules:
Insights & consulting module
Insights audit report (IAR) – comprehensive fleet assessment including 7 reports on all aspects of fleet operations
Vehicle module that includes:
- Powertrain evaluation (IAR 1 battery electric versus fuel cell)
- Federal & state vehicle incentive assessment
- Vehicle assessment (IAR2) including current fleet type, age & options
- Repower engineering of ICB vehicles (battery electric or fuel cell conversion of internal combustion engines & bus reconditioning)
- Vehicle maintenance
- New vehicle sales (battery electric or fuel cell)
- Vehicle market – trade in on ICB vehicles for conversion & resale
- Vehicle training (drivers, technicians, controllers)
- Fleet management including telematics & fleet & asset management software
- Vehicle finance, lease & partnership solutions
Infrastructure module includes::
- Infrastructure evaluation (IAR 3 & IAR 4)
- Electric versus Hydrogen infrastructure evaluation
- Federal & state infrastructure incentive assessment
- Grid availability & pricing analysis
- Hydrogen supply assessment
- Route & charge station analysis
- Depot versus on-route charge station analysis
- Modular charge station supply, engineering & maintenance ( Electric & Hydrogen)
- Infrastructure command & control systems
- Training (charge station/H2 depot technicians, controllers )
- Infrastructure finance, lease & partnership solutions
Power module includes::
- Infrastructure evaluation (IAR 3 & IAR 4)
- Electric versus Hydrogen infrastructure evaluation
- Federal & state infrastructure incentive assessment
- Grid availability & pricing analysis
- Hydrogen supply assessment
- Route & charge station analysis
- Depot versus on-route charge station analysis
- Modular power station supply, engineering & maintenance ( Electric & Hydrogen with PV or biomass powered)
- Infrastructure command & control systems
- Training (electric/H2 technicians, controllers )
- Infrastructure finance, lease & partnership solutions
Fleet management module includes:
Open system architecture enabling seamless integration with legacy telematics & systems
- Fleet management systems evaluation (IAR 5)
- Data-driven efficiency & Mobility electrification methodologies
- IoT powered integrated fleet management
- Seamless integration to existing telematics systems
- Fleet performance optimization (reduced fuel & maintenance costs)
- Training (telematics, software & controllers )
- Fleet management finance, lease & partnership solutions
- Modular systems enabling comprehensive command & control on all aspects of fleet operations including
- Telematics
- Fleet, infrastructure & asset management
- Expense & cost control
- Employee scheduling, training & wages
- Customer booking, payment collection & experience
Training & qualification module
- Most advanced and complete education within the industry
- Fully accredited qualifications and specialised new-skills programs.
- Built on the world’s number 1 LMS platform (Learner Management Software)
- Headed up by industry experts
- Dynamic global content and training delivery with localization of accreditations
- Most current and relevant international technology and skills requirements.
- Training includes workplace experience through global & local partners
- Work-ready skills that advances the industry
- Highest level of employment security and earnings.
Bank & Business module
Bank & Business module
EVC provides dynamic project finance, business model & partnership options.
Partnership options include:
- OMT (Operate-Maintain-Transfer)
- BT (Build Transfer)
- BOT (Build Operate Transfer)
- LDO (Lease-Develop-Operate)
- BOLT (Build-Operate-Lease-Transfer)
- BOOT (Build Own Operate Transfer)
- BOO (Build Own Operate).
According to Capterra a good rule of thumb is that companies should spend anywhere from 1 to 5% of their total salary cost on training, depending on how much they want to emphasize training in their organization. In South Africa the skills development levy is 1% of salaries.
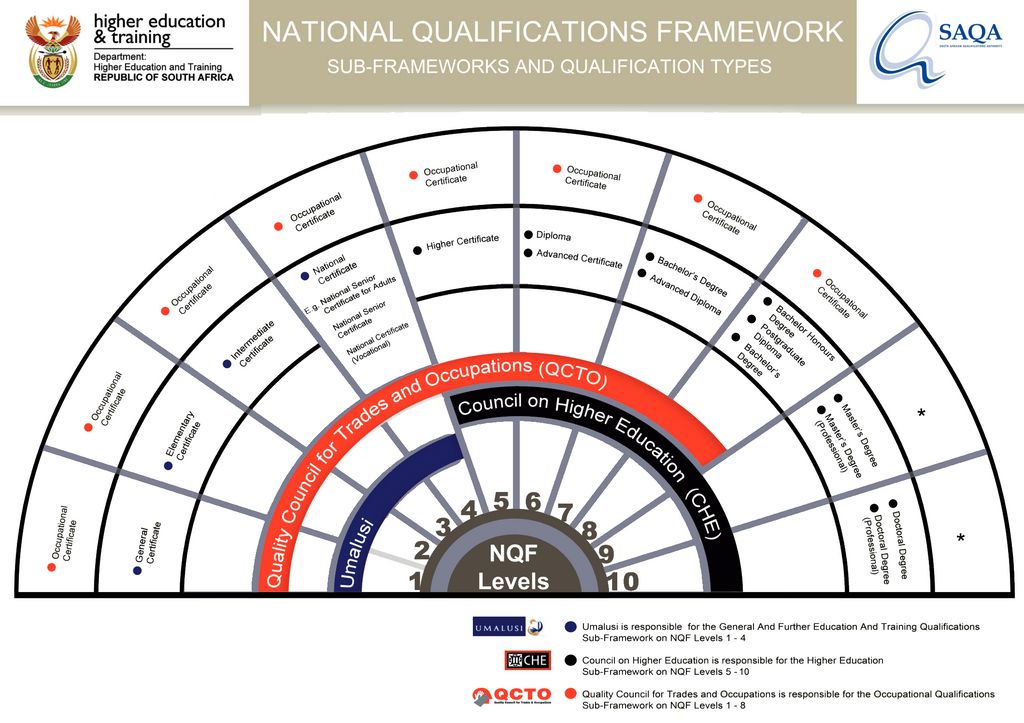
South Africa’s public entity responsible for quality assurance and the oversight of the design, accreditation, implementation, assessment and certification of occupational qualifications, part-qualifications and skills programmes. The Quality Council for Trades and Occupations (QCTO) is a Quality Council established in 2010 in terms of the Skills Development Act (Act 97 of 1998) as amended in 2008. The QCTO also offers guidance to skills development providers (private and public) and assessment centres who must be accredited by the QCTO in order to implement occupational qualifications.
The QCTO is responsible for the following
- Establishment and management of the Occupational Qualification Sub-framework (OQSF)
- Accreditation of Skills Development Providers
- Research and Knowledge Development
- Certification
- Occupational Qualifications development and maintenance
- Accreditation of Assessment Centres
- Stakeholder Management and Advocacy
- Assessment
Occupational Qualifications Sub-Framework (OQSF), which is one of the three integrated sub-frameworks of the National Qualifications Framework. SAQA registers occupational qualifications on the OQSF as recommended by the QCTO.
The QCTO is responsible for the accreditation of Skills Development Providers (SDPs) to offer the following programmes and qualifications that fall under the Occupational Qualifications Sub-Framework (OQSF). Any SDP offering training – or who wants to provide training – in any of the QCTO qualifications/ part qualifications must seek accreditation from the QCTO, and must comply with the minimum criteria for
Accreditation. Accreditation is valid for a period of five years from the date on which the QCTO granted accreditation to the SDP or until the SDP is de-accredited by the
QCTO. The accreditation may be withdrawn by the QCTO if the SDP fails to perform its responsibilities as stipulated in the QCTO Accreditation Policy, and/or contravenes the provisions stipulated in the accreditation letter or act in a way that is unlawful or unbecoming of a SDP.
The South African Qualifications Authority (SAQA) is the oversight body of the NQF and the custodian of its values and quality character. The role of SAQA, as stipulated in the NQF Act, is to advance the objectives of the NQF, oversee the further development and implementation of the NQF, and co-ordinate the Sub-Frameworks. SAQA’s functions are set out in section 13 of the NQF Act.
The National Qualifications Framework (NQF) is the system that records the credits assigned to each level of learning achievement in a formal way to ensure that the skills and knowledge that have been learnt are recognised throughout the country. A national qualifications framework (NQF) is a formal system describing qualifications. 47 countries participating in the Bologna Process are committed to producing a national qualifications framework. Other countries not part of this process also have national qualifications frameworks.
Australia
The Australian Qualifications Framework is the national qualifications framework in Australia.
United Kingdom
The current national qualifications frameworks in the UK are:
England: Regulated Qualifications Framework (RQF) for general and vocational qualifications regulated by Ofqual
Northern Ireland: Council for the Curriculum, Examinations and Assessment (CCEA)
Wales: Credit and Qualifications Framework for Wales (CQFW) for all qualifications.
Scotland: Scottish Credit and Qualifications Framework (SCQF) for all qualifications.
The Frameworks for Higher Education Qualifications of UK Degree Awarding Bodies (FHEQ) for qualifications awarded by bodies across the United Kingdom with degree-awarding powers
Ireland
The National Framework of Qualifications is the framework used in Ireland.
New Zealand
The New Zealand Qualifications Framework, administered by the New Zealand Qualifications Authority, covers qualifications in secondary and tertiary education[24] in New Zealand.
A learnership is a learning programme that leads to an occupational qualification.
Learnerships include classroom-based learning at a training centre or college and on-the-job training in a workplace. For you to participate in a learnership, the key thing to be in place is that there must be an employer willing and able to provide the work experience.
People leaving schools and colleges, unemployed people and people already in jobs.
There is no charge for a person to go on a learnership. Everyone selected for a
a learnership programme must receive a learner allowance paid by the employer.
The length of a learnership will differ but will normally not be less than one year.
The learner is placed in a learnership and signs a learnership agreement with an
employer, which states the rights and responsibilities of the learner when following the learning programme.
The employer provides the work experience part of the learnership and signs
the same learnership agreement stating the employer’s rights and responsibilities,
including agreements on the level of the learnership allowance.
Training providers provide the training on behalf of the employee and sign the same
legal agreement stating the training provider’s rights and responsibilities.
A Sector Education and Training Authority (SETA) organises and facilitates the funding of learnerships in a specific area of the economy.
If the learnership is completed successfully, you will have a qualification that is recognised throughout the county. To prove that you have the qualification you will be given a certificate.
If you are unemployed when the learnership begins, there is no guarantee of a job at the end. After the learnership, you gain a qualification and work experience and you become more employable than before.
The Department of Labour recruits, selects and refers unemployed people who meet the minimum criteria for a particular learnership to employers looking for learners. Register with the Department of Labour as a work seeker at any labour centre.
SETA” stands for Sector Education and Training Authority. The functions and responsibilities of SETAs are set out in Chapter 3, section 10 the Skills Development Act, 1998. Their main function is to contribute to the raising of skills, to bring skills to the employed, or those wanting to be employed, in their section. They have to do this by ensuring that people learn skills that are needed by employers and communities. There is no value in training people if they cannot use the skills they have learnt. Training and skills development is not just for young people starting their first jobs, though it is important for them too! The skills of people already in jobs must also be enhanced. Training must be to agreed standards and within a national framework wherever possible. It is no good if someone is trained in one province and their qualifications are not recognised in another. It is not ideal for one employer to increase the skills of his or her staff if another employer does not recognize them. All training, wherever it is provided should be subject to quality control and where appropriate be compared to the best international standards.
In order to achieve these objectives the Skills Development Act states that the functions and duties of a SETA are to:
Develop a skills plan
Implement its sector skills plan
Promote learning programmes
Register agreements for learning programmes
Perform functions delegated to it by QCTO
Disburse levies collected from employers and their sector
Liaise with National Skills Authority on policy, strategy and sector skills plan
The National Skills Authority is a statutory body that was first established in 1999 in terms of Chapter 2 of the Skills Development Act 1998. The Skills Development Act assigned the Skills development responsibility under the Minister for Higher Education and Training. The strategic objectives include promoting skills development and profiling the work of the NSA through communication & marketing.
A prerequisite for recognising any points under Skills Development on your BEE scorecard is the submission of a Workplace Skills Plan (WSP), Pivotal Plan and Annual Training Report (ATR) prior to the deadline in April each year.
What is Skills Development Facilitation?
The process by which a Skills Development Facilitator (SDF) analyzes, prepares, executes, and reports on the numerous training activities in an organization is known as skills development facilitation. A skills development facilitator has Seta-related responsibilities for the organization’s design, delivery, and reporting of training.
Skills development facilitation includes some of the following aspects:
- confirming that the appropriate SETA has registered your company.
- Submitting an annual Workplace Skills Plan (WSP), Pivotal Plan and Annual Training Report to ensure eligibility for mandatory grants awarded by your SETA.
- yearly claims to your SETA for your particular industry.
- Learnership programs offered by RSE that are completely accredited provide a comprehensive cycle of training and development.
- introducing youth subsidies, learnerships, and other programs for skill development.
- creating and submitting reports and an employment equity plan.
- helping to create committees for training and/or employment equity.
SDF and BEE scorecard
Businesses in South Africa who want to achieve or maintain a satisfactory BEE level and also comply with the criteria of the Skills Development Act have made skills development a strategic focus.
The following must be submitted in order for any points under “Skills Development” on your BEE scorecard to be recognized:
- Workplace Skills Plan (WSP);
- Pivotal Plan;
- Annual Training Report (ATR) prior to the deadline in April each year depending on the SETA.
Businesses will only gain points for submitting workplace skills plans after they can demonstrate that they did so. The WSP and Pivotal Plan must also have SETA approval in order to qualify for any points on the BEE scorecard, according to the newly modified BEE Codes.
The law as it stands mandates that any company with yearly payroll above R500 000 (including director fees) must pay SARS 1% of their payroll, which SARS would subsequently distribute to the relevant SETA with which the company is registered.
For socially and economically disadvantaged people in South Africa, learning and skills development programs are funded by the Skills Development Levy (SDL). You will benefit from a workforce that is more educated and more productive if your organization encourages learning and growth in the workplace.
By Paying Skills Development Levies you qualify for skills development grants (mandatory and discretionary);
- A Mandatory Grant would reimburse you for 20% of your levy.
- Discretionary Grants can be used to claim 50% of your levy (Learnerships, Skills Programmes, Apprenticeships, Workplace Experience Placements, Internships and Bursaries)
- substantial tax allowances when you implement learnerships in your company;
- a 12H tax rebate of up to 50% for employing persons below the age of 29 (youth subsidy) under certain circumstances;
- a further R80 000 as an additional tax expense to be recouped on all registered learnership programmes;
- an increase in your B-BBEE compliance level
Businesses that are not aware of the aforementioned incentives and claim procedures will lose out on significant profits.
Businesses in South Africa who want to achieve or maintain a satisfactory BEE level and also comply with the criteria of the Skills Development Act have made skills development a strategic focus.
The following must be submitted in order for any points under “Skills Development” on your BEE scorecard to be recognized:
- Workplace Skills Plan (WSP);
- Pivotal Plan;
- Annual Training Report (ATR) prior to the deadline in April each year depending on the SETA.
Businesses will only gain points for submitting workplace skills plans after they can demonstrate that they did so. The WSP and Pivotal Plan must also have SETA approval in order to qualify for any points on the BEE scorecard, according to the newly modified BEE Codes.
Facilitator: To facilitate the development of an employer’s skills development strategy.
Expect: to serve as an expert resource for accrediting the employer as a training provider and for the implementation of appropriate learnerships and skills programmes.
Administrator: to complete and submit the WSP and ATR.
Advisor: to advise the employers and employees on the National Skills Development Strategy (NSDS) on the implementation of the WSP.
Education and needs evaluation: to assess the skills development needs of the organisation.
Mediator: to serve as a contact person between the employer and the relevant Seta
The Mandatory Grant serves a vital purpose. Employers are encouraged to give data to their SETA about their workforce and skills needs based on their annual Workplace Skills Plans (WSPs) and Annual Training Reports (ATRs).
The SETA is required to return 20% of the Skills Development Levy to firms that successfully make their required submissions each year.
The remaining 49.5% of the Skills Development Levy is distributed to companies at the SETAs’ discretion. Employers must apply for this financing through their respective SETA’s appropriate channels.
Submission via the relevant SETA’s online portal, mailing a Letter of Intent (LOI), and responding to SETA submission windows are examples of these channels. Each SETA outlines how applications for these funds will be received.
These funds are designed to encourage stakeholders and businesses to contribute to skill development, address important and scarce skill shortages, and create jobs and employment opportunities
Real change through strong leadership.
We create a talent management and hiring strategy that works for you and map out your potential talent pool. Our goal to work alongside customers to realize sustainable transformation projects in South Africa is a crucial component of our personnel management. In order to accomplish this, we develop an internal talent pool of qualified individuals from which we may draw in order to strategically succeed with important employees, should they decide to leave the company for any reason. By doing this, it is made sure that the enabling strategies won’t be significantly disrupted while the organization’s aims are met.Real change through strong leadership. We create a talent management and hiring strategy that works for you and map out your potential talent pool.
Our goal to work alongside customers to realize sustainable transformation projects in South Africa is a crucial component of our personnel management. In order to accomplish this, we develop an internal talent pool of qualified individuals from which we may draw in order to strategically succeed with important employees, should they decide to leave the company for any reason. By doing this, it is made sure that the enabling strategies won’t be significantly disrupted while the organization’s aims are met.
Attracting and retaining the right talent
EVC address the underlying causes of potential labour turnover and help companies with the ability to sustain their workforce to continuously meet the business strategy in a manner befitting the corporate culture. It is unrealistic to attempt to retain all employees, as there must be some movement of talent and labor in the organization.
New hires bring new expertise and ideas, which is beneficial since it helps an organization stay inventive. This does not imply, however, that there should not be a broad customer and employer value proposition, as this framework should bring together current employees and those looking to join. Companies should put more emphasis on enticing key individuals to stay rather than establishing a fixed quantitative goal for enhancing employee retention. Setting a goal to keep the best employees who support the company’s business strategy and organizational culture is one example.
- Talent acquisition methodology: the manner in which talent acquired for clients maximizes retention possibility from the outset
- Employer and customer value proposition creation
- Talent identification in line with the business strategy and organizational culture
- Talent assessments: business and culture strategy aligned, competency-based, psychometric, personality and emotional intelligence skills assessments
- Coaching: appropriate coaching tailored to individual development needs
An accredited work readiness programme for persons with disabilities (PWDs) contributes to your skills development scorecard.
EVC is dedicated to the advancement of individuals with disabilities. The EVC work readiness Bootcamp enables you to invest in the skill development of your personnel as well as the employability of job-seeking prospects. Despite the fact that the program can be customized to assist everyone, it has been specially created to address the unique issues faced by People Living with Disabilities (PWDs), who are more susceptible to barriers to entry in the labour market. EVC is a great way to make sure that candidates, including those with disabilities, are empowered and employable.
The EVC work preparedness program gives job seekers a distinctive educational opportunity. This SETA-accredited program offers a diverse selection of modules in a way that encourages participation and gives applicants the essential employability skills they need to compete effectively in a job market that is dynamic and ever-changing while pursuing certification.
Learnership project Management across all sectors:
- Learner Recruitment, Placement and Registration,
- Orientation and workplace essentials
- Full cycle Learnership facilitation with external providers,
- External moderation,
- Seta Tranche and stipend administration
- Facilitation for learner external exam,
- Learner exit and assistance with permanent job placements
Our 12- to 36-month, industry-specific and generic learnership programs are especially created for companies that want to maximize their BEE points and be eligible for additional bonus points, as well as those that want to be eligible for additional learnership tax refunds and SETA financing.
These skill-building initiatives have been shown to maximize SDL reimbursements, boost revenue and cash flow, and guarantee a more motivated and productive workforce.
Qualifying for tax rebates from SARS as per section 12H of the Income Tax Act, translating into R80 000 per standard Learnership and R120 000 per Disabled Learnership;
Access to an Employment Tax Incentive (ETI) of R1 000 per month per employee aged 18 – 29 years – offset against your PAYE
- Learner exit and assistance with permanent job placements
We have developed a fail proof solution to assist organization through the change and to optimize their skills development funding options
Each project and organization is unique and has its particular needs and challenges. Each context needs its own implementation model.
To help organizations navigate the transformation and maximize their funding possibilities for skill development, we have created a fail-safe five-step strategy.
Identify your organization’s unique offering, selling point and and skills development pathway
Determine the special selling point and career path of your organization.
Determine the needs, specializations and career paths offered by your organization.
Accreditation assistance provided n the following industries: Services, Wholesale and Retail, Agriculture, Information Technology, Health and Welfare, Manufacturing and Engineering, Transportation, Early Childhood Education, Fiber processing and Manufacturing, Banking, Insurance, Finance and Hospitality, we provide clients and training providers with accreditation services from transitioning from SETA’s to QCTo as well as QCTO accreditation.
We collaborate with QCTO and the following Quality Partners.
- Services Seta
- WRSETA
- Agriseta
- MICT Seta
- HWseta
- MERSETA
- TETA
- ETDP
- NAMB
- FPSETA
- Bankseta
- CHIETA
- Construction seta
- SASSeta
- MERSETA
- FASSET
- EWSETA
- FOODbev
- CATHSSETA
- MQA
- INSETA
Transition from SETA accreditation or new QCTO accreditation Assistance
- Legal entity /juristic person established in terms of South African law at the time of seeking accreditation Possible evidence: Proof of CIPRO registration;
- Valid tax clearance certificate issued by SARS
- Provide proof of financial sustainability for the learning services applied for and throughout the accreditation period; Possible evidence: audited financial statements, financial surety, business plan, if applicable;
- Have a valid Occupational Health and Safety certificate, if applicable
- Provide evidence of appropriately qualified human resource/s to deliver the qualifications; Possible evidence: CVs, certified ID and certified qualifications,
- Proof that the institution has all the relevant resources as per curriculum requirements. ( to complete Annexure h, g, j and E of QCTO documents aligned with the qualification content, a list of resources for practical and theoretical training at the institution)
- Learner Management System which can generate reports
- Complete accreditation SETA/QCTO application form on behalf of your company. Annexure A, G, H & E submission including learner Material Matrix
- Supply and customize the Quality Management System (QMS)
For each of our clients’ unique demands and requirements, as well as taking into account the company’s characteristics, EVC creates a custom quality management system. All QCTO-required policies and procedures are included in the Special Quality Management system.
- Basic conditions of employment act
- Appeals Policy and procedure – ASA001
- Assessment policy and procedure – ASS001
- Asset control policy and procedure – ACP001
- Certification Policy and procedure – CPP001
- Customer and Marketing policy and procedure – CMP001
- Design and Development of Assessment Material Policy and Procedure – DDP001
- Design and Development of Training Material Policy and Procedure – DDT001
- Document Record Management and Database Policy and Procedure – DRM001
- Evaluation of training and Assessment Material Policy and Procedure – ETA001
- Facilitation Policy and Procedure FPP001
- Financial Management Policy and Procedure FMP001
- Health and Safety Policy and Procedure HSP001
- HIV Policy – HIV001
- Learner Entry, Disability, support and confidentiality policy and procedure LSC001
- Learner Grievance Policy and Procedure – LPG001
- Minutes of Quality Assurance Meeting MM001
- Moderation Checklist MC001
- Moderation Plan Checklist MPC001
- Moderation Policy and Procedure MPP001
- Monthly staff QMS report – QMS002
- Off-Site occupational health and safety checklist – OHSC001
- Off-site Training and Assessment Policy and Procedure- OST001
- Program Design and Development Policy and Procedure- PDD001
- QMS Policy and Procedure –QMS001
- Quarterly Management Review Report – QMS003
- Recognition of Prior Learning Policy and Procedure – RPL001
- Recruitment and Selection Policy and Procedure – RSP001
- Review Mechanism Policy and Procedure – QMS005
- Staff Performance and Appraisal Policy and Procedure – SPA001
- Staff Selection, Training and Development Policy and Procedure – STD001
- Training Committee Policy and Procedure -QMS004
- Training needs analysis – TNA001
Sourcing and training of facilitators, assessors and Moderators
EVC helps with the documentation that must be submitted with the application as well as with the training of subject-matter experts for the Assessor and Moderator programs.
Deliver SAQA-aligned training guides or help institutions align their material with Occupational Qualification outcomes.
- During the accreditation process, deal with the SETA/QCTO for clarification and handle all corrections to the learning materials and other issues.
- Pre-Site Visit Consultation for Training Facility Preparation to Ensure Compliance with SETA Standards.
- SETA/QCTO guaranteed accreditation.
The South African skills development sector is undergoing significant change with the Quality Council for Trades and Occupations (QCTO) taking over accrediting, implementing, evaluating, and certifying occupational qualifications, part-qualifications, and skills programs. This change will significantly impact businesses and workforces.
The new QCTO certifications aim to improve the quality of the training and qualifications by being more tailored and specific to the learner’s occupational profile. This change will require new accreditation from historical qualifications to occupational qualifications with QCTO as well as effect learnership delivery. EVC understands this change and wants to see you succeed. We are here to guide you through this significant change and provide the services you need to successfully transition and navigate the new landscape
EVC offers all-encompassing E-learning system training on the Moodle platform for facilitators, assessors, and moderators. EVC has successfully accredited qualifications in E-learning with QCTO, Services SETA, WRSETA, ETDP, CATHSSETA, and AgriSETA. Documents for e-learning accreditation are specially tailored to each organization’s specific needs. Moodle is the world’s most customisable and trusted open source learning management system used by hundreds of millions of learners worldwide
For facilitators, assessors, and moderators, EVC provides comprehensive Moodle platform training for e-learning systems. Qualifications in e-learning have been successfully accredited by EVC with the QCTO, Services SETA, WRSETA, ETDP, CATHSSETA, and AgriSETA. Documents for e-learning accreditation are uniquely suited to the requirements of each institution.
E-Learning Program Strategy
E-Learning Quality Management System
E-learning Facilitator Assessor Guide
Assessment Assessor and Moderator Guide
Outcome Based Education, Assessment & Moderation Process Flow
Electronic Form Templates and training on digital signature for learners, assessors and moderators.
- Learner Assessment Plan
- Pre-Assessment Meeting Checklist
- Personal Narrative
- Learner Feedback form
- Assessment decision and Declaration
- Evaluation of Assessment
Student Management System
Student Handbook
Learnership project Management across all sectors:
Learner Recruitment, Placement and Registration,
Orientation and workplace essentials
Facilitation of full cycle Learnerships, skills programs and short courses,
Facilitation of External moderation
Facilitation of Seta Tranche payments and stipend administration
Facilitation of learner external EISA and TRADE examinations,
Learner CV writing and Interview preparation job placement assistance
Full grant application pack and business model for discretionary and special projects.
FRANCHISEES
TRANSFORMING
THE FUTURE
#1 NET-ZERO FLEET TECHNOLOGY
Complete modular solution integrating all aspects of net-zero fleet transition
ACCELERATE NET-ZERO
SERVICE MODULES

ENGINEERING MODULES
Modules


Insights
Quantified insights audit report with impact study on all areas required to make enlightened decisions of a fleet transition to electric (battery electric or fuel cell).

Fleet management
Data-driven efficiency & Mobility electrification methodologies. IoT powered integrated fleet management. Seamless integration to existing telematics systems.

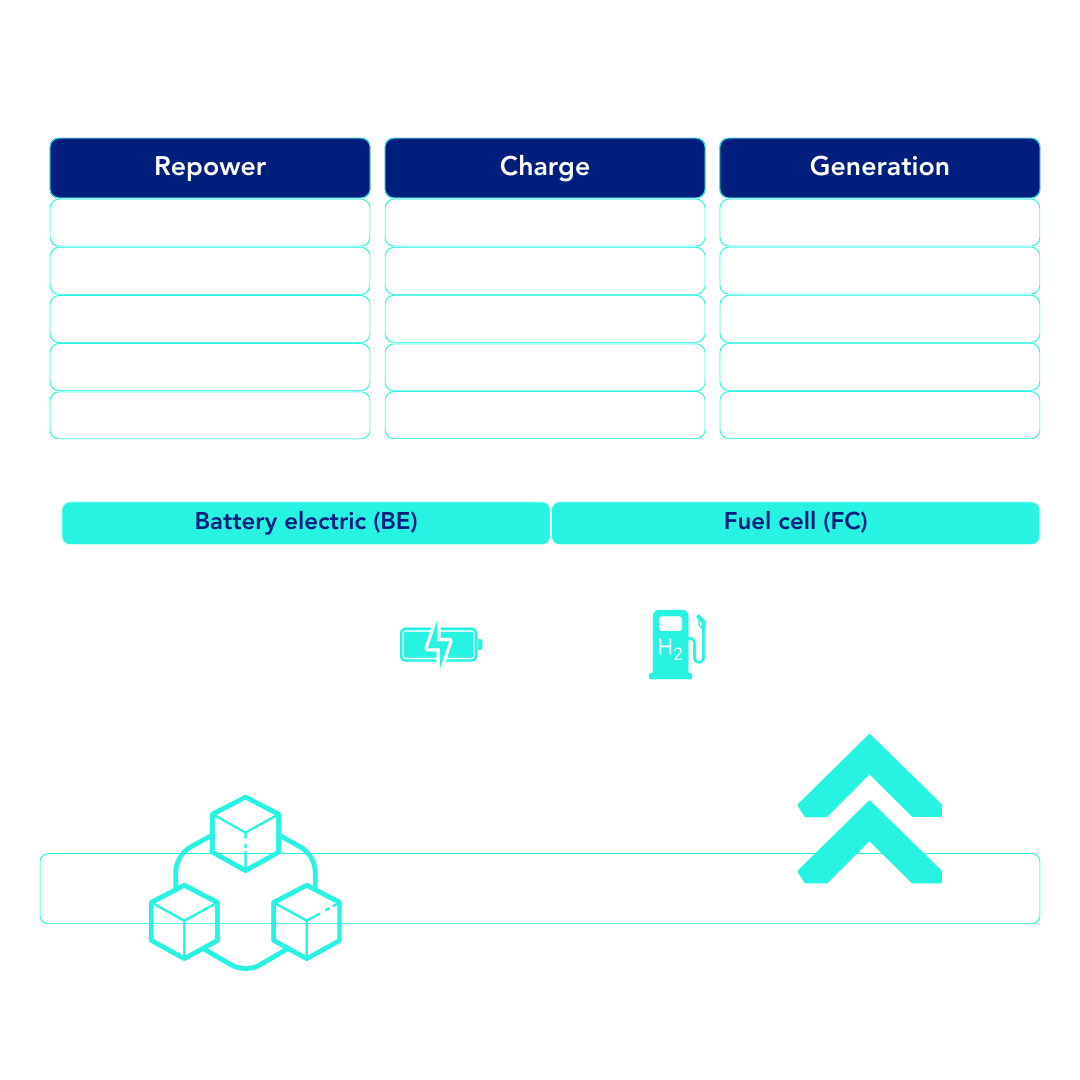
Repower
Transform your fleet to a net-zero electric powered fleet. Repower options include battery electric or fuel-cell powertrains with trade-in or new vehicle options.

Trade
New & trade-in market. International brands & OEM. Trade-ins of internal combustion engine vehicles. Conversions & reconditioning to electric.
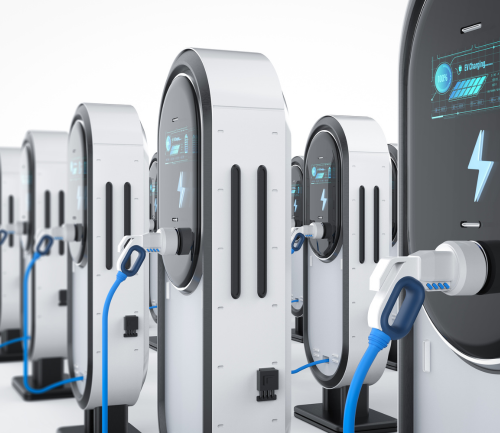

Charge
Electric & hydrogen fleet charge stations. Complete modular infrastructure solution. AC & DC Fast Charge. Turnkey hydrogen dispensing stations. Compression, storage, cooling, and H2 dispensing modules.
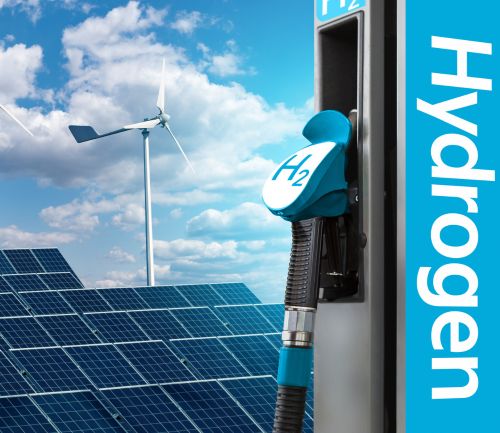

Generation
Electricity & hydrogen production modules. EV transition adding pressure on electrical grids. Modular power generation options. Adapted based on location and output requirements.

Finance
Dynamic green finance, grant & carbon credit management. Franchise financing, new electric fleet, repowering & reconditioning, energy storage & charging infrastructure, generation assets, fleet management & skills development.

Academy
Electric fleet engineering & operational skills. Fully accredited QCTO qualifications. Full spectrum specialized EV courses. Powered by the number 1 e-learning platform.
Insights & consulting
ICE (internal combustion engine) transition
Conversion to battery electric (BEV) & fuel cell vehicles (FCV)
Includes federal, state & local impacting factors
Vehicle age, route & workload assessment
Insights audit report (IAR) quantified detailed impact study:
- Powertrain (ICE to BEV/FCV)
- Vehicle (new vs repowered investment)
- Infrastructure (grid & H2 availability & pricing)
- Energy production ( electricity & H2 process analysis)
- Fleet systems (telematics & fleet & resource management)
- Skills development (operators. technicians, controllers +)
- Business model (finance, implementation & partnership options)
Vehicle
Powertrain evaluation ( BEV vs FCV)
Federal & state vehicle incentive assessment
Vehicle assessment (current fleet type, age & options)
Repower engineering of ICB vehicles
Vehicle maintenance
New vehicle purchases
Vehicle market (trade in on ICB for conversion & resale)
Skills development (drivers, technicians, controllers)
Fleet systems (telematics & fleet & asset management)
Vehicle finance, lease & partnership solutions
Infrastructure
Modular charge stations ( Electric & H2)
Electric & H2 infrastructure evaluation & solutions
Infrastructure command & control systems
Training (charge station/H2 depot technicians, controllers )
Infrastructure finance, lease & partnership solutions
Federal & state infrastructure incentive assessment
Grid availability & pricing analysis
Hydrogen supply assessment
Route & charge station analysis
Depot versus on-route charge station analysis
Power production
Modular power stations (engineering & maintenance)
Electric & H2 output modules
PV, wind & biomass powered
Electric & H2 infrastructure assessment
Federal & state power incentive assessment
Grid availability & pricing analysis
Hydrogen supply assessment
Feedstock supply agreements
Local resource analysis including biomass, sun & wind
Power command & control systems
Training (electric/H2 technicians, controllers )
Infrastructure finance, lease & partnership solutions
Fleet management
Open modular system architecture
Seamless integration with legacy systems & telematics
Fleet management evaluation
Data-driven efficiency & mobility electrification methodologies
IoT powered integrated fleet management
Fleet performance optimization (reduced fuel & maintenance costs)
Training (telematics, software & controllers )
Fleet management finance, lease & partnership solutions
Command & control on all aspects of fleet operations
Skills development
Most advanced education within the green mobility industry
Fully accredited qualifications
Specialised new-skills programs
Built on the world’s leading e-learning platform
Headed up by industry experts
Dynamic global content and training delivery
Localization of accreditations
Workplace experience through global & local partners
Work-ready skills that advances the industry
Highest level of employment security and earnings
Finance & business model
Dynamic project finance, business model & partnership options
Partnership options include OMT, BT, BOT, LDO, BOLT, BOOT & BOO
EVC franchise provides advanced plug-in-play transformation
Supplement & transform ICB powered business model
Incorporate state-of-the-art BEV & FCV technology
Superior global supply chain of quality product and services
Dynamic on-line skills development platform
World-class support structure
New product and services revenue streams
Improve customer offering & satisfaction
Employee job satisfaction, employment security & higher income
Increased enterprize competitiveness & profitability
Customers
Virtually every citizen on the planet is a potential client with the net-zero mobility transition. Evolution, technology, local resources & infrastructure and applicable federal and state incentives directly impact client focus areas that include:
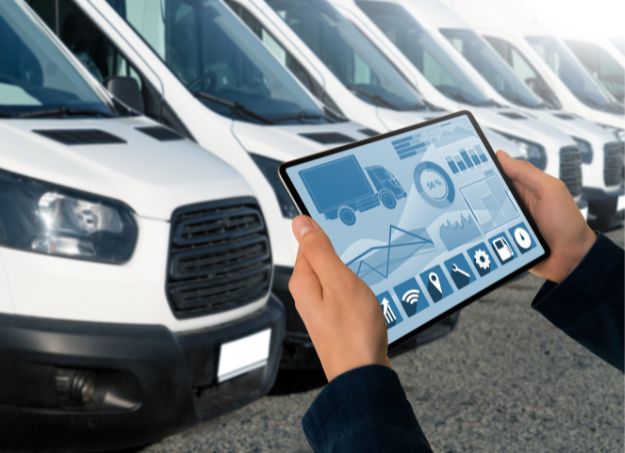

Fleets
Public & private fleet operators.
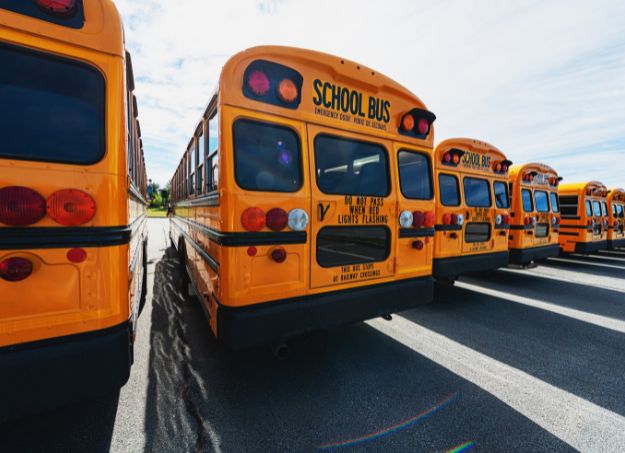

Schools
School bus conversions are a high priority area.

City bus
City bus transition to electric is highly effective.

Courier
Courier service vehicles & infrastructure.

Minibus taxis
Repowering, charge infrastructure & generation

Hospitals
Ambulances & 1st responders.

Airports
Airport transit vehicles & customer ev charge.

Municipalities
Transition internal combustion fleet to electric.

Auto rental
Transition of vehicles & infrastructure .

Taxi & Flexride
Transition to smart cities.

Supermarkets
Food & convenience delivery transition to electric.

Truckers
Transition to net-zero fleet & infrastructure.

Bulk movers
Transition bulk vehicles & infrastructure

Farms
Transition to a net-zero production

Military
Transition to a net-zero defense force.

Auto sport
Transition of sport & recreational vehicles.